1 不同任务类型的提交方式
首先体现了Executor这个抽象接口的功能,实现解耦
- 提交任务的线程只关注于提交这个动作,任务提交完,使命就结束了
- NioEventLoopGroup负责关注任务的管理和调度
- 所谓的管理就是如何在内存中组织编排任务实例
- 调度就是负责实现任务如何执行
名词(术语)约定,在Netty世界中,任务有2种
- IO任务(特指的是Socket编程涉及的网络IO)
- 其他都叫做普通任务(或者叫其他任务)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
private static void test00() {
NioEventLoopGroup eg = new NioEventLoopGroup();
eg.execute(() -> System.out.println("execute::任务-普通任务"));
eg.submit(() -> System.out.println("submit::任务-普通任务"));
eg.schedule(() -> System.out.println("schedule::任务-定时任务-一次性"), 10_000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
eg.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> System.out.println("scheduleAtFixedRate::任务-定时任务-周期性"), 10_000L, 10_000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
eg.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> System.out.println("scheduleWithFixedDelay::任务-定时任务-周期性"), 10_000L, 10_000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
eg.register(new NioSocketChannel());
}
|
2 任务的提交
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
this.next().execute(command);
}
|
1
2
3
4
| @Override
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
return this.next().submit(task);
}
|
1
2
3
4
| @Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return this.next().schedule(command, delay, unit);
}
|
1
2
3
4
| @Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit) {
return this.next().scheduleAtFixedRate(command, initialDelay, period, unit);
}
|
1
2
3
4
| @Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return this.next().scheduleWithFixedDelay(command, initialDelay, delay, unit);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return this.next()
.register(channel);
}
|
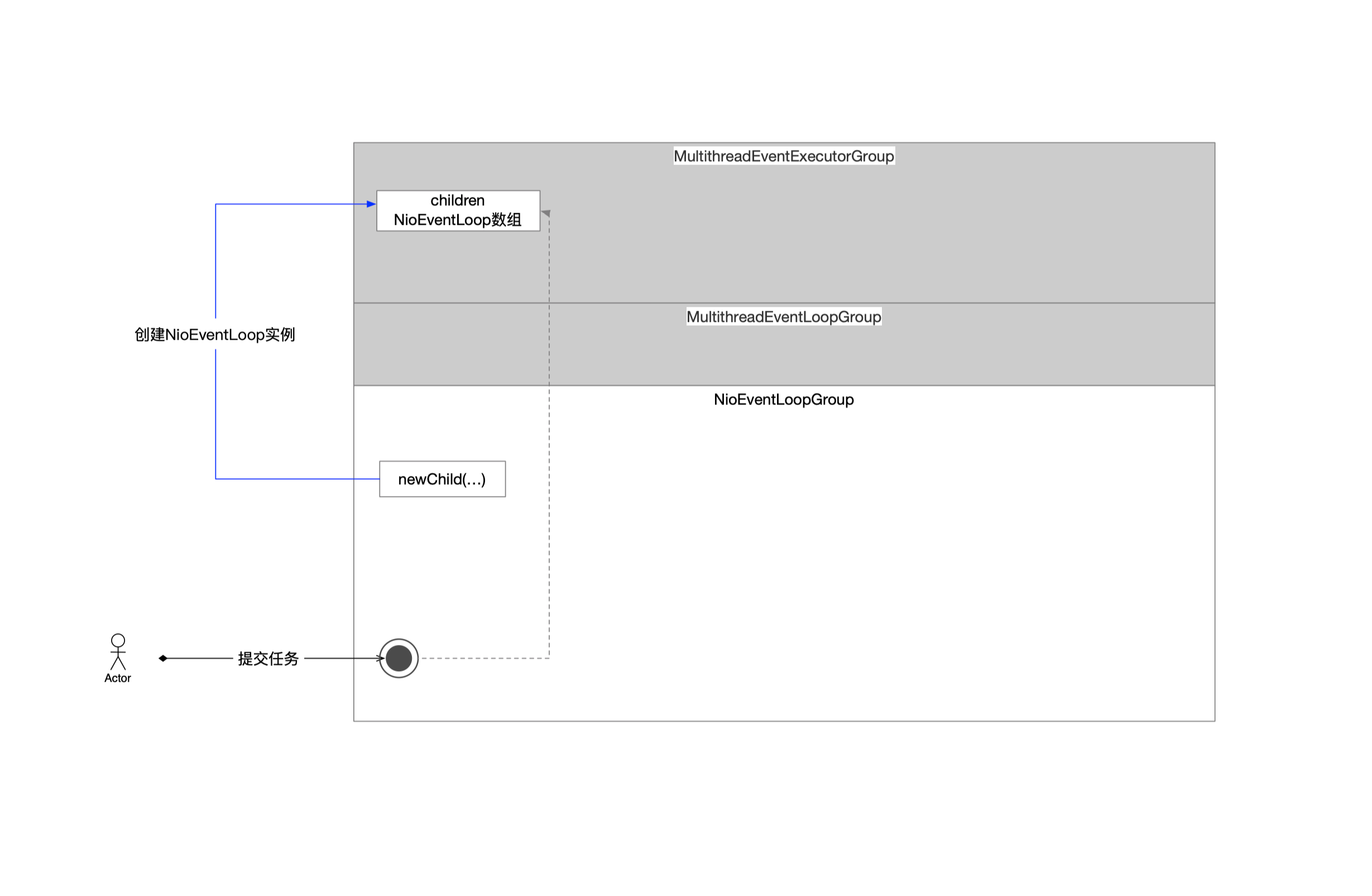
综上,在任务提交这件事情上,NioEventLoopGroup不进行实质性的流程处理,真正干活的是NioEventLoop这个组件。
3 总结
NioEventLoopGroup组件只开放了跟客户端交互的窗口,只负责传达提交任务的指令,后续跟任务生命周期相关的流程已经跟NioEventLoopGroup没有关系了,都是由NioEventLoop组件负责,即
- NioEventLoop负责任务的管理
- NioEventLoop负责任务的调度
- NioEventLoop负责任务的执行