Redis-0x05-ziplist
数据类型的编码方式。
1 ziplist是什么
1.1 结构
从注释上可以看出ziplist结构如下。
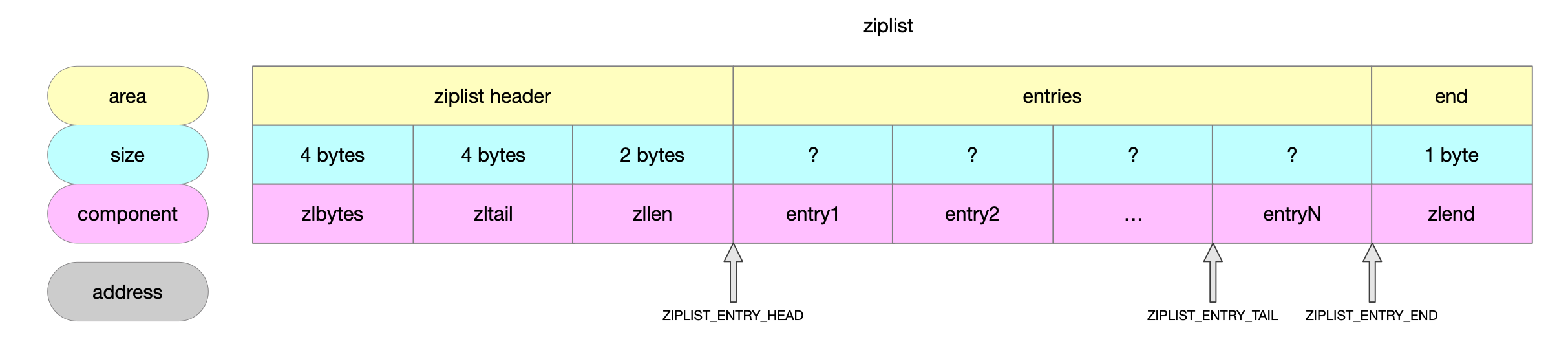
1.2 字段解释
| 字段 | 长度 | 语义 |
|---|---|---|
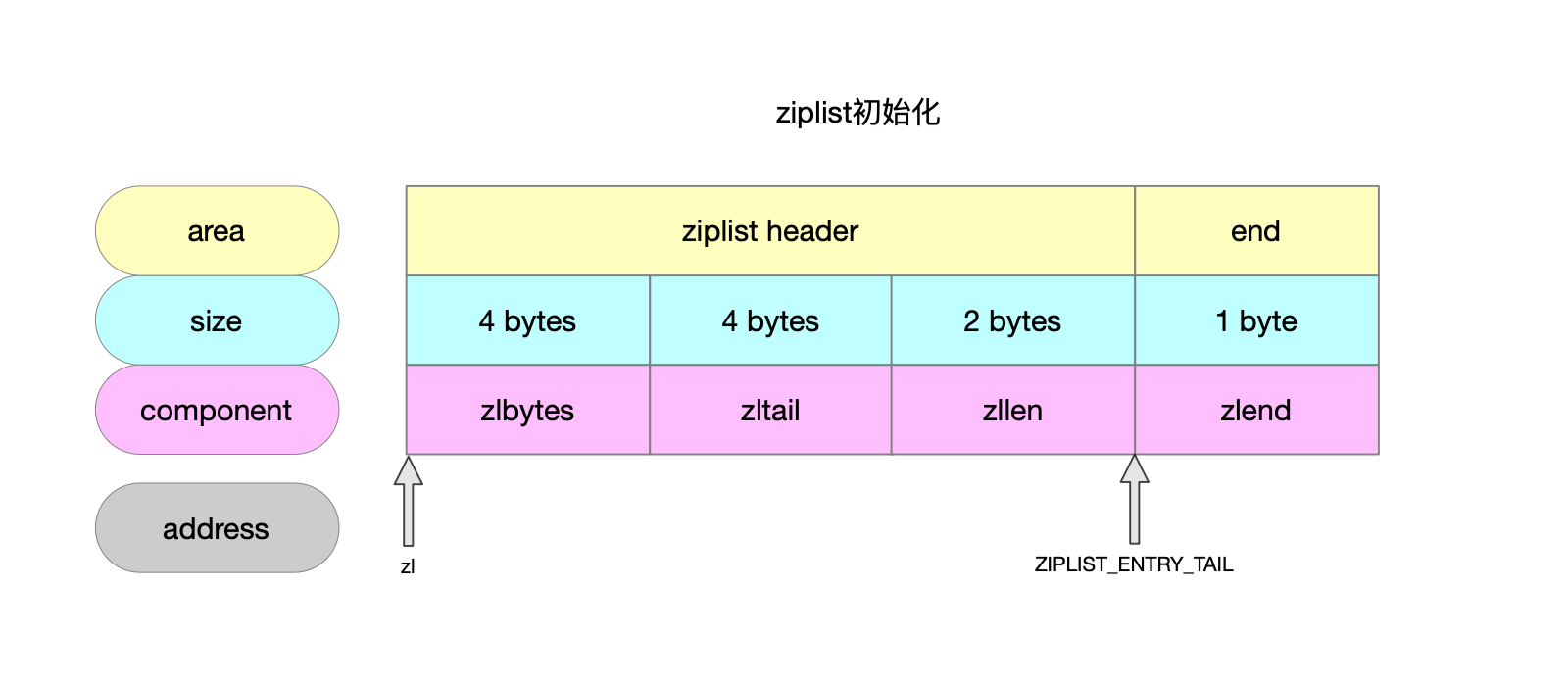
| zlbytes | uint32_t | 表示ziplist占用内存大小。 |
| zltail | uint32_t | 表示最后一个entry相对ziplist的地址偏移量。 |
| zllen | uint16_t | entry节点数量,16bit上限是2^16-1。 数量<上限,代表的就是实际节点数量。 数量>=上限,节点的实际数量需要遍历计数。 |
| entry | - | 保存有限长度的字符串或者整数。 |
| zlend | byte | 0xFF,特殊的节点,ziplist的结束标识。 |
2 entry是什么
2.1 结构
从注释上可以看出entry的结构如下。
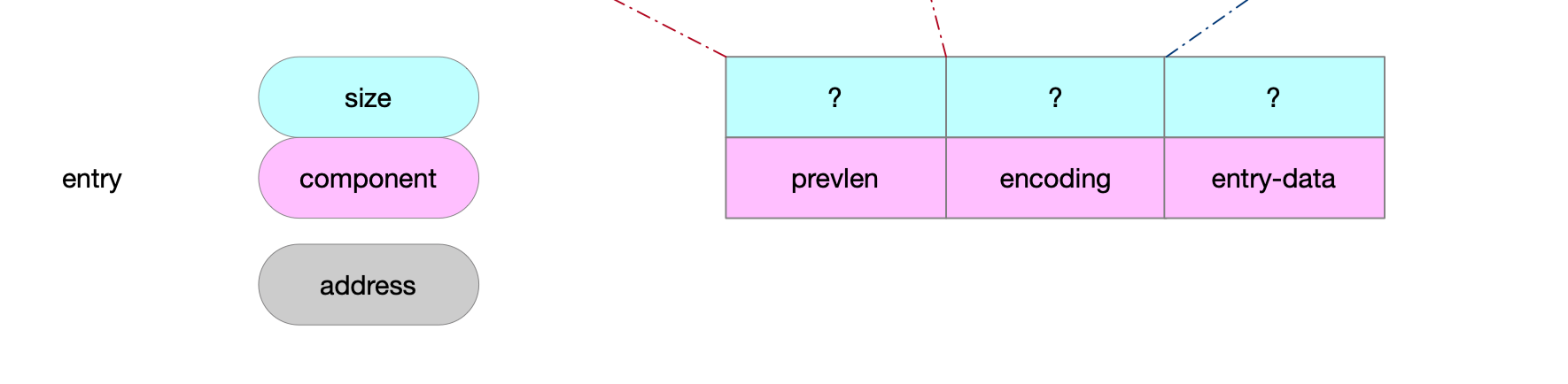
2.2 字段解释
| 字段 | 语义 |
|---|---|
| prevlen | 前驱节点entry占用多少bytes。 |
| encoding | 主要作用区分存储的内容是整数还是字符串。 存储字符串的时候,还承担着表示字符串长度的职责。 存储整数的时候,可能还用来直接存储内容。 |
| entry-data | 节点实际存储的内容。 以字符数组形式存储的字符串,不需要\0结束标识符。 整数。 |
2.3 详解
2.3.1 prevlen字段
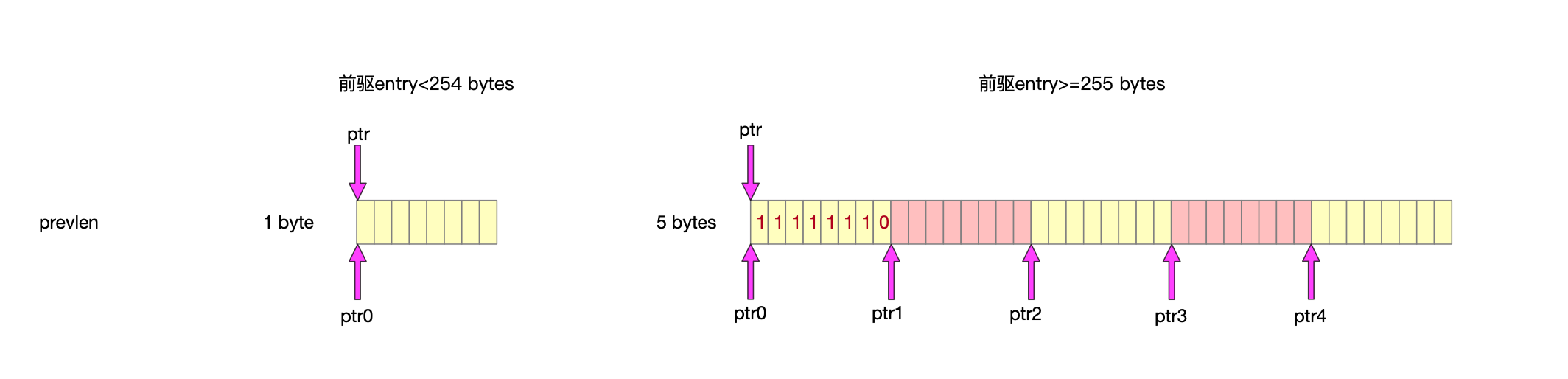
为什么要在entry上冗余着前一个entry的内存大小,其实作用就跟双链表的指针差不多,这儿不用指针关联,只要记录上一个节点多少个字节就可以移动指针,往前寻址了。
前驱entry地址=当前entry地址-前驱entry大小
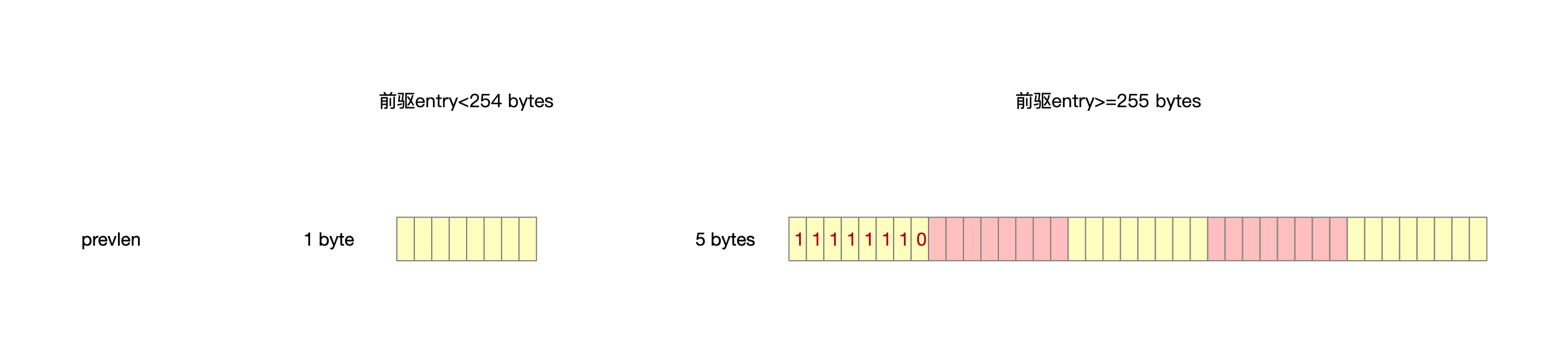
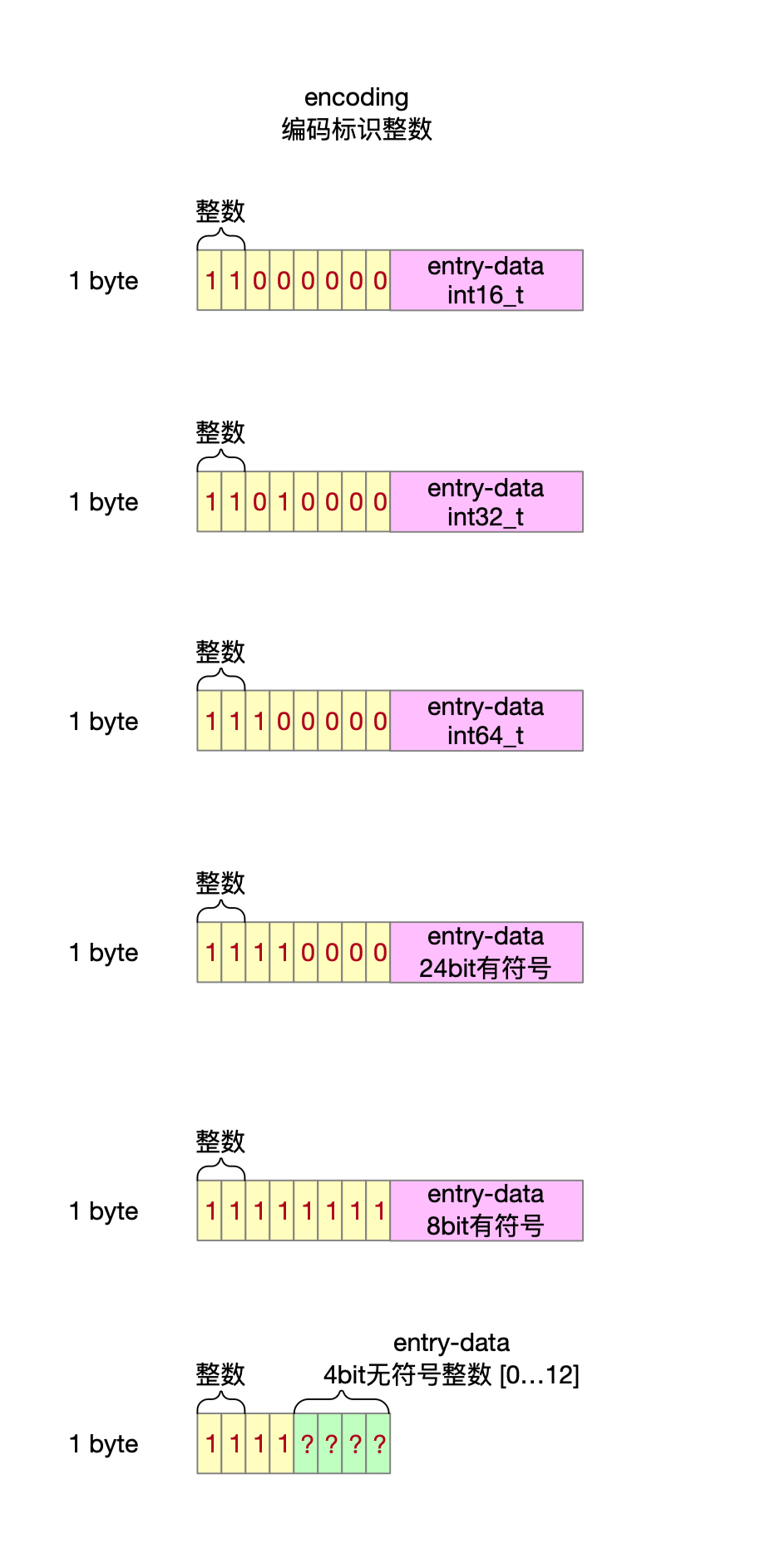
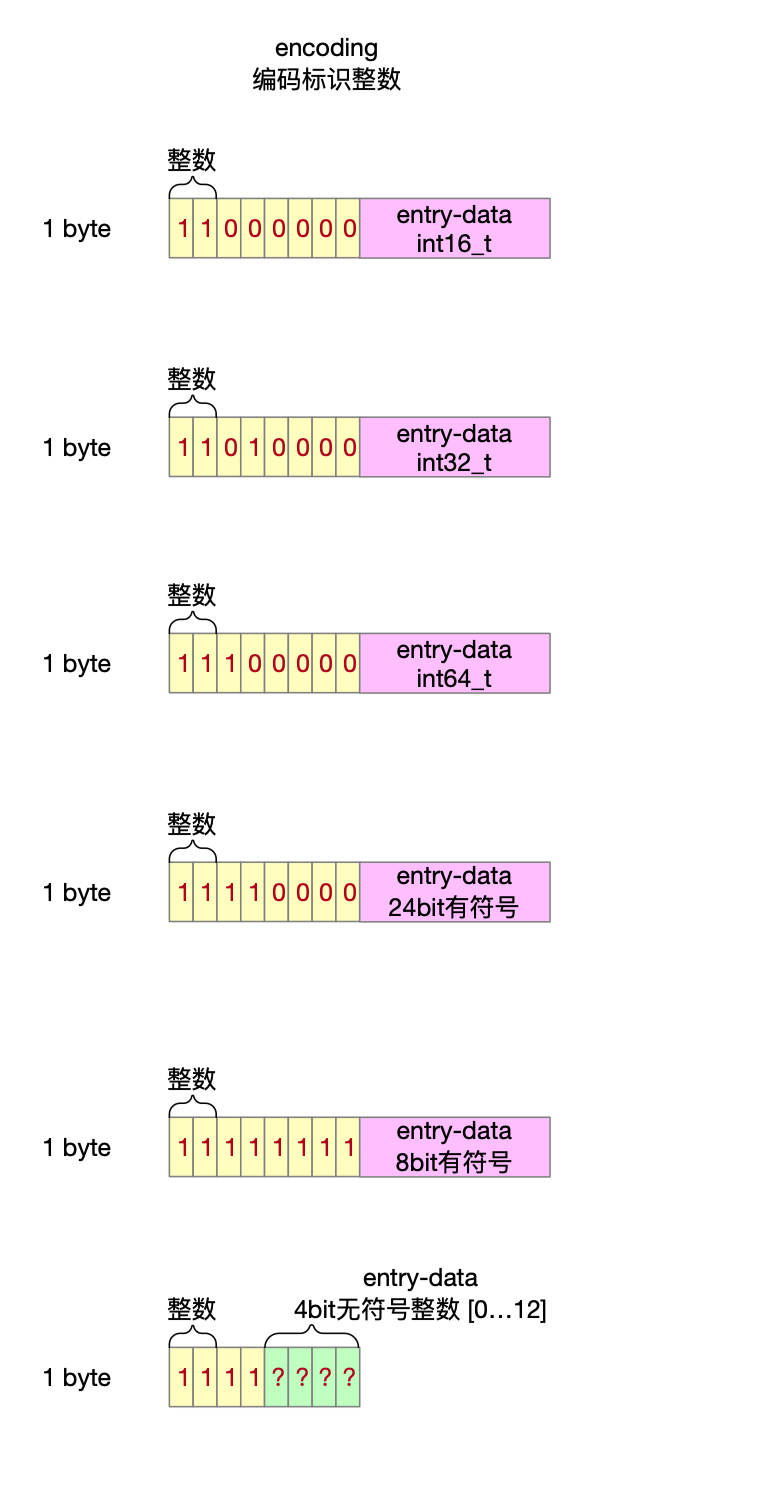
2.3.2 encoding字段
encoding二进制表示形式的高2位作为标识位,决定entry中数据内容是字符数组还是整数。
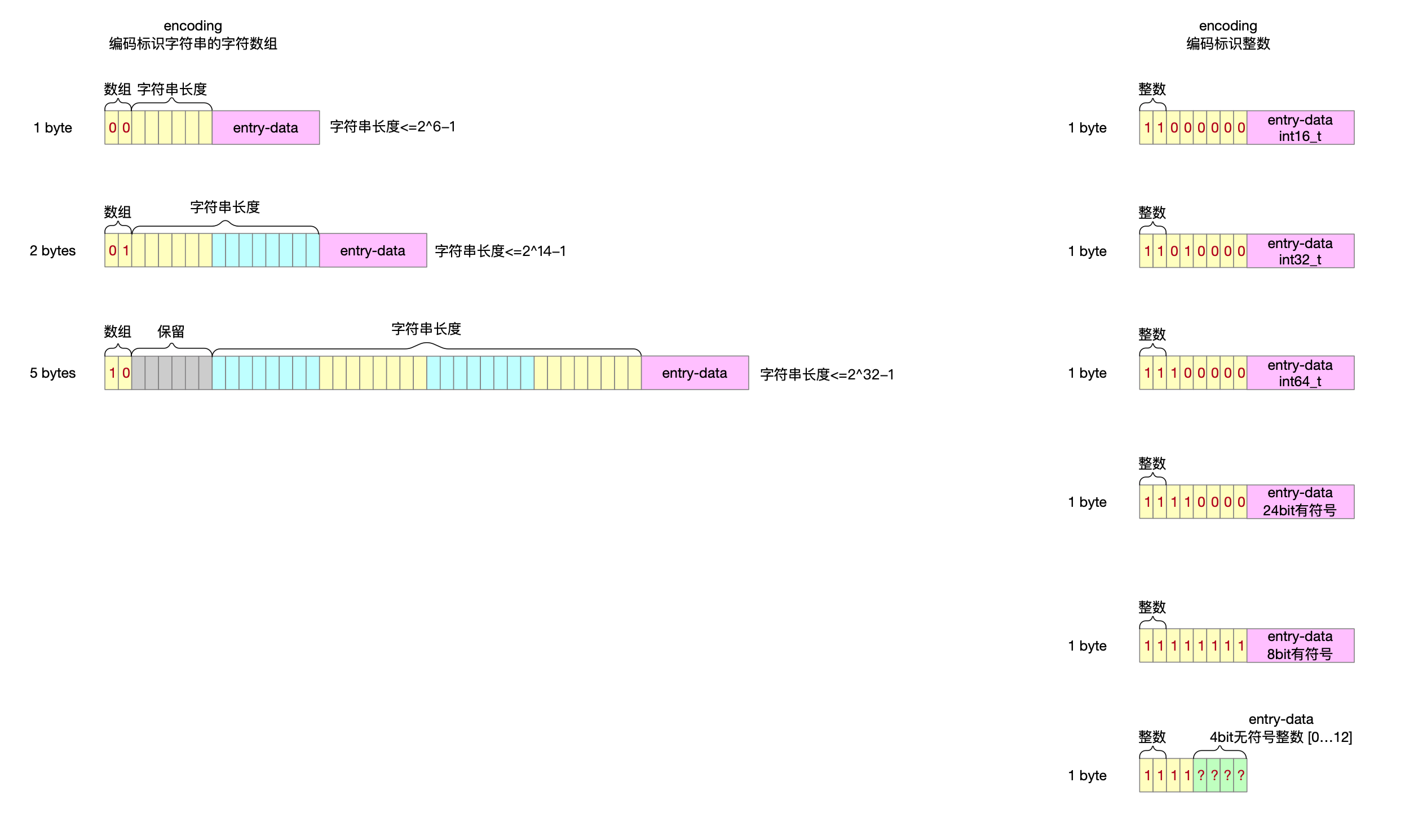
2.3.2.1 存储字符串
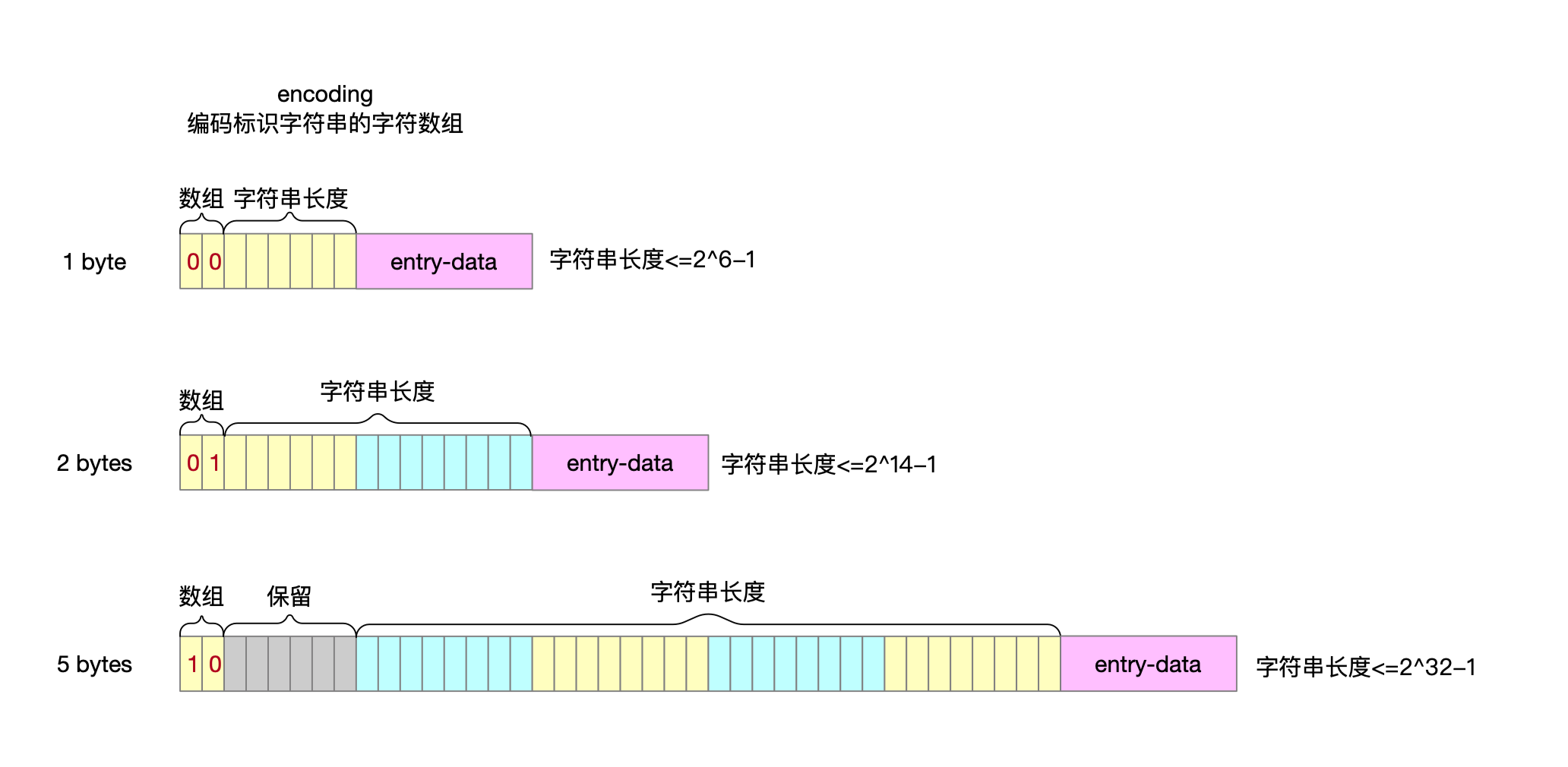
2.3.2.2 存储整数
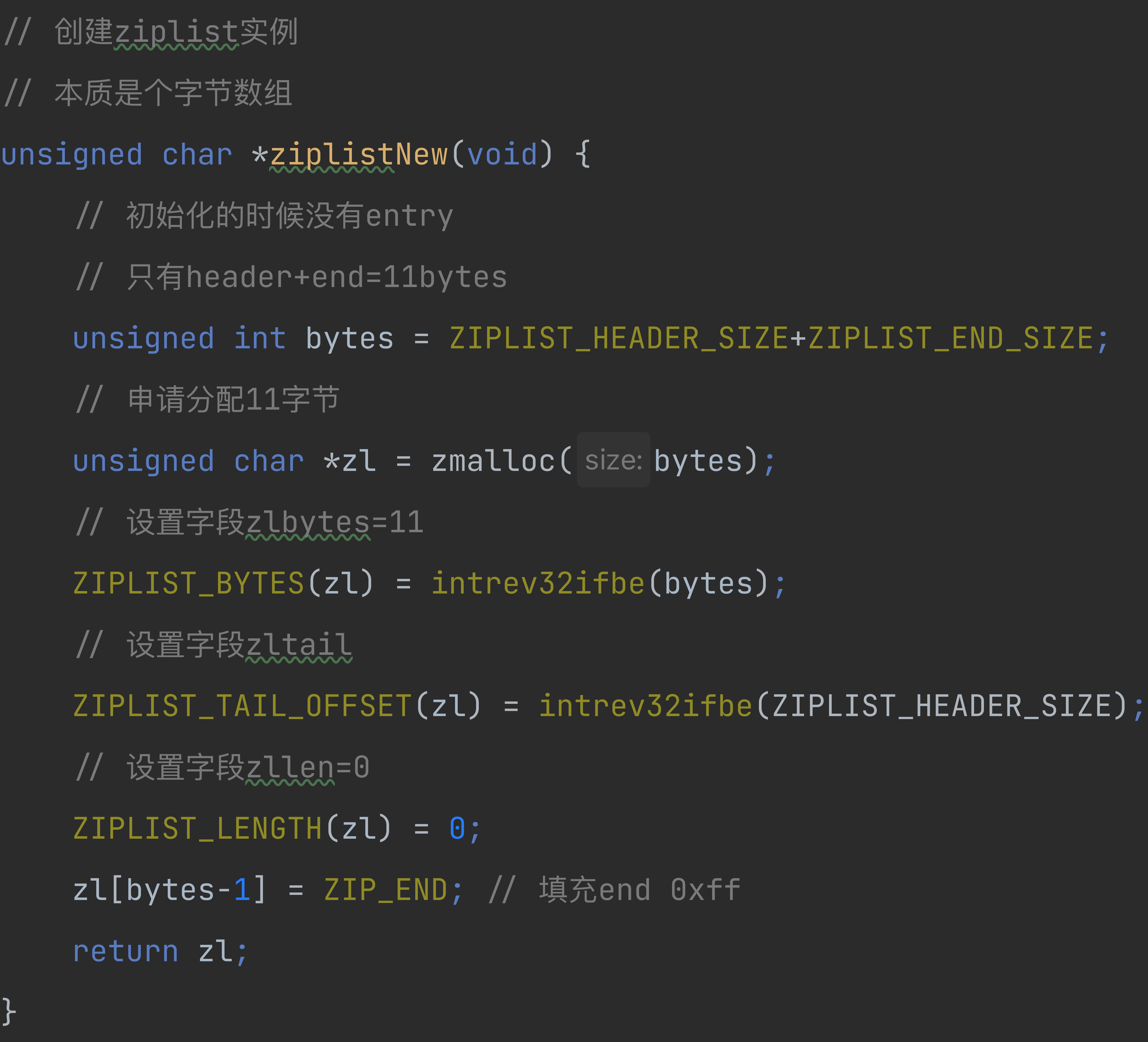
3 初始化ziplist
4 entry字段prevlen
4.1 prevlen前驱长度编码
c
1 | |
4.2 prevlen前驱长度
c
1 | |
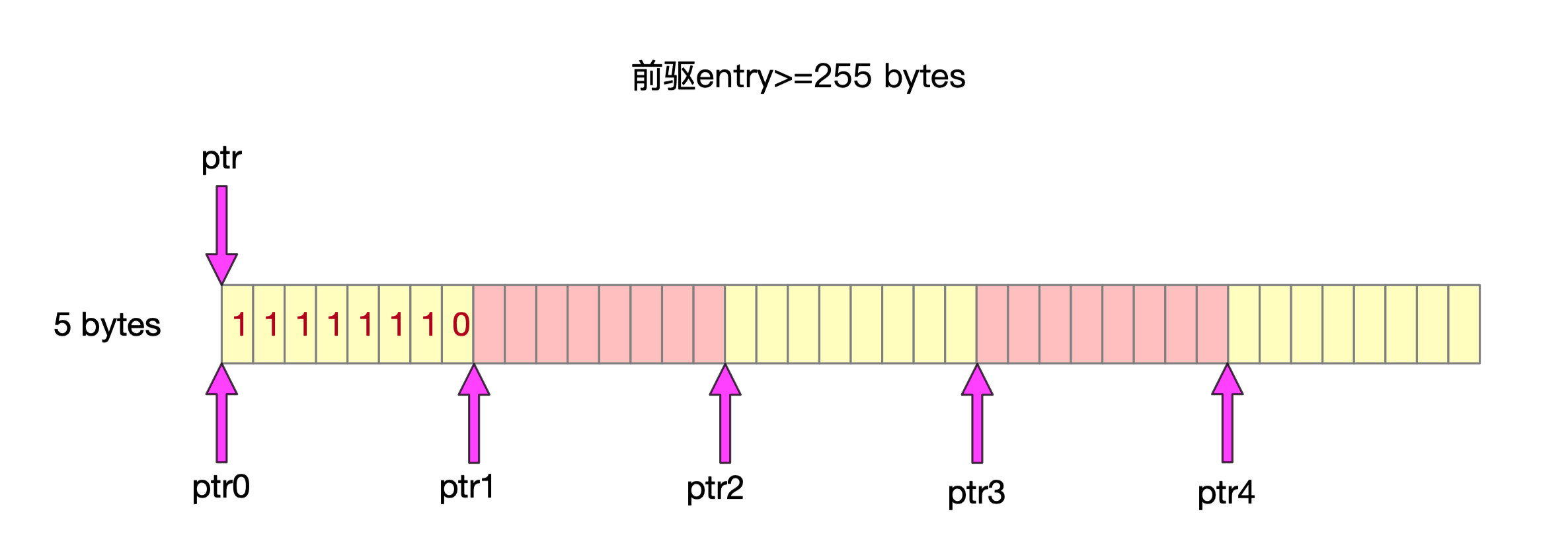
4.3 prevlen需要多大内存 && prevlen字段写入
c
1 | |
c
1 | |
5 entry字段encoding
5.1 编码类型
c
1 | |
5.2 encoding需要多大内存 && encoding字段写入
c
1 | |
6 entry字段entry-data
6.1 entry-data需要大多内存
6.1.1 字符串
entry-data中存储字符串,不需要给字符数组申请结束标识\0。
c
1 | |
6.1.2 整数
c
1 | |
6.2 entry-data字段写入
6.2.1 字符串
c
1 | |
6.2.2 整数
c
1 | |
7 ziplist大小重置
c
1 | |
8 添加节点
8.1 任意位置插入节点
c
1 | |
8.2 头插\尾插
c
1 | |
9 按照脚标查找元素
c
1 | |
10 entry节点的后继节点
c
1 | |
11 zlentry
11.1 数据结构
c
1 | |
11.2 示意图
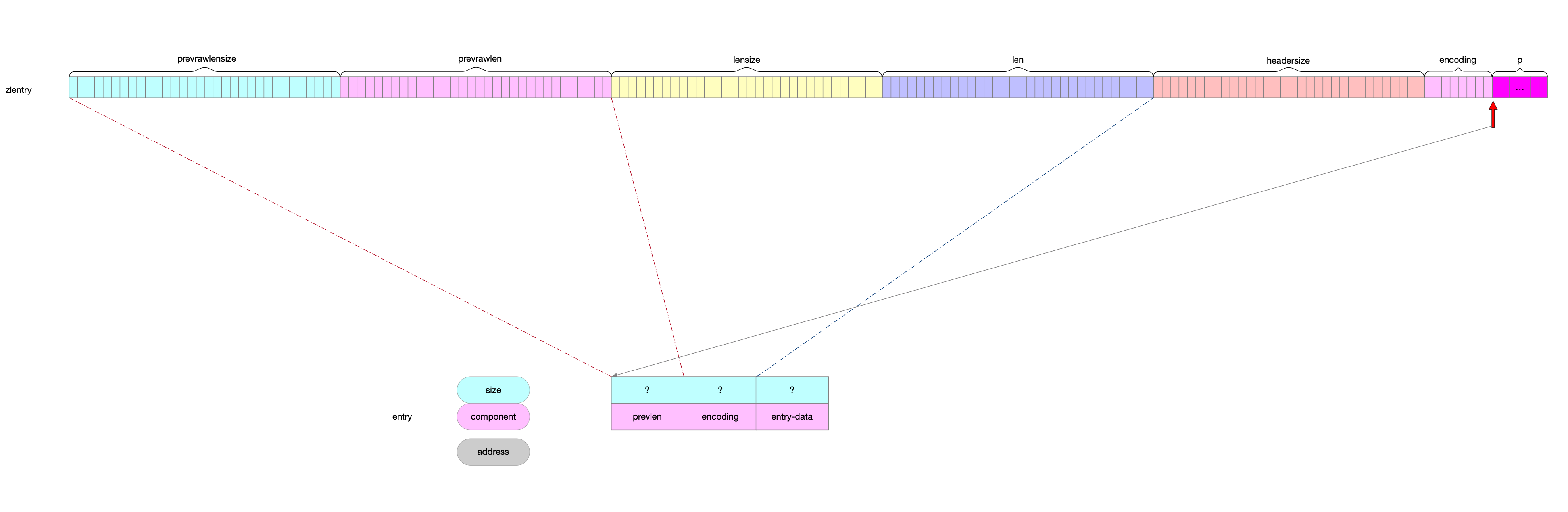
11.3 数据结构转换
11.3.1 entry信息写到zlentry
c
1 | |
11.3.1.1 entry中prevlen字段解析到zlentry中prevrawlensize和prevrawlen
c
1 | |
c
1 | |
11.3.1.2 entry中encoding字段解析到zlentry中encoding字段
c
1 | |
11.3.1.3 entry中encoding和data-entry字段解析到zlentry中lensize和len字段
c
1 | |
11.3.2 entry信息写到zlentry并校验
c
1 | |
11.4 entry所占内存
c
1 | |
12 读取entry节点中的元素
c
1 | |
13 读取entry节点中整数元素
c
1 | |
Redis-0x05-ziplist
https://bannirui.github.io/2023/03/30/Redis-0x05-ziplist/