1 阻塞队列API
|
Throws exception |
Special value |
Blocks |
Times out |
| Insert |
add(e) |
offer(e) |
put(e) |
offer(e, time, unit) |
| Remove |
remove() |
poll() |
take() |
poll(time, uint) |
| Examine |
element() |
peek() |
|
|
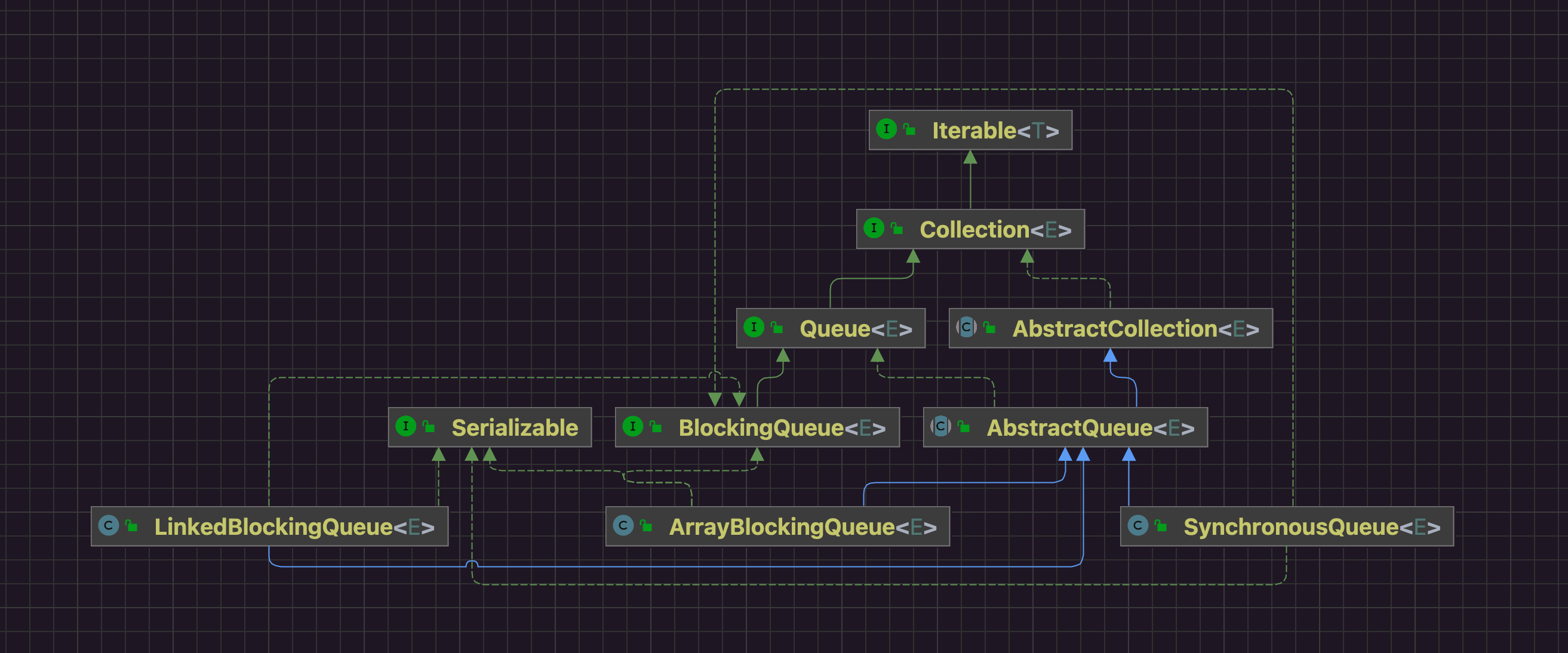
2 类图
3 构造方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
final Object[] items;
int putIndex;
int count;
final ReentrantLock lock;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
private final Condition notEmpty;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
private final Condition notFull;
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
|
ArrayBlockingQueue使用的数据结构是数组,通过两个指针移动控制元素入队出队,循环往复。
阻塞的实现依赖于ReentrantLock的条件队列。
4 API
4.1 put
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
Objects.requireNonNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
this.enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
private void enqueue(E e) {
final Object[] items = this.items;
items[this.putIndex] = e;
if (++putIndex == this.items.length) putIndex = 0;
this.count++;
this.notEmpty.signal();
}
|
4.2 take
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
return this.dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
private E dequeue() {
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E e = (E) items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length) takeIndex = 0;
count--;
if (this.itrs != null)
this.itrs.elementDequeued();
this.notFull.signal();
return e;
}
|
5 总结
|
ArrayBlockingQueue |
| 数据结构 |
数组 |
| 是否有界 |
有界,必须指定大小初始化数组 |
| 锁实现 |
ReentrantLock |
| 锁数量 |
1 |
| 线程阻塞机制 |
ReentrantLock条件队列阻塞/通知唤醒 |
| 生产者消费者用锁 |
共用同一个锁 |
