摘要
1 AQS是什么 摘自java doc,简而言之就是该类基于阻塞队列为同步锁的实现提供了框架功能
1 Provides a framework for implementing blocking locks and related synchronizers (semaphores, events, etc) that rely on first-in-first-out (FIFO) wait queues.
从注释描述以及类名AbstractQueuedSynchronizer可预见的几个特点
该类是个抽象类,使用了模板方法的设计模式定义了整体框架功能,预留了一部分接口的空实现或者抽象方法延迟到子类实现
实现了队列功能
线程同步临界资源
2 使用方式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 public class MyLock {public static void main (String[] args) {long tid = Thread.currentThread().getId();MyLock myLock = new MyLock ();try {"[" + tid + "]上锁" );"[" + tid + "] thread running..." );try {3_000 );catch (InterruptedException e) {finally {"[" + tid + "]去锁" );private final MySync mySync = new MySync ();private static final int step = 1 ;public void lock () {this .mySync.acquire(step);public void unLock () {this .mySync.release(step);private static class MySync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {@Override protected boolean tryAcquire (int arg) {int c = super .getState();Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();if (c < 0 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException ();if (c == 0 ) {if (!super .compareAndSetState(0 , arg)) return false ;else {super .setExclusiveOwnerThread(curThread);return true ;else {if (Objects.equals(curThread, super .getExclusiveOwnerThread()))throw new UnsupportedOperationException ();else return false ;@Override protected boolean tryRelease (int arg) {Thread curThread = Thread.currentThread();if (!Objects.equals(curThread, super .getExclusiveOwnerThread())) throw new UnsupportedOperationException ();int c = super .getState();if (c == 0 || c - arg != 0 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException ();if (!super .compareAndSetState(c, 0 )) return false ;super .setExclusiveOwnerThread(null );return true ;
3 源码原理 大体的思路是从ReentrantLock这个工具类着手
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class AQSTest {private static ReentrantLock fairLock = new ReentrantLock (true );private static ReentrantLock nonfairLock = new ReentrantLock (false );public static void main (String[] args) {public void testFairLock () {try {finally {public void testNonfairLock () {try {finally {
跟踪代码就要有主次先后顺序
公平锁和非公平锁的实现差异,公平锁要保证的边界肯定要比非公平锁多的,非公平锁的性能理论上也要优于公平锁的
锁重入的实现方式
队列的实现方式
线程实例的处理方式
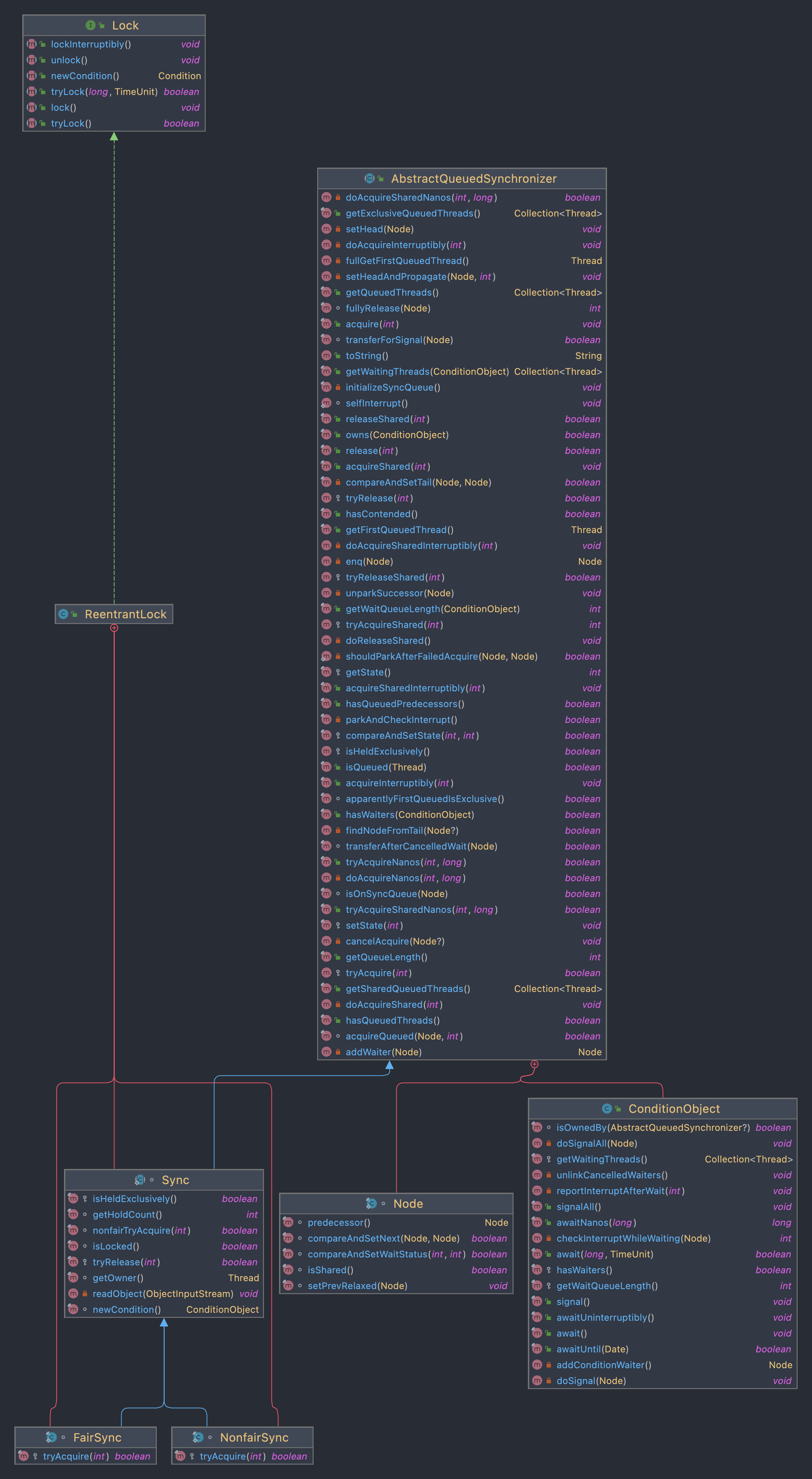
3.1 类图
Lock定义了ReentrantLock的顶层抽象,我们只关注#lock(…)和#unLock(…)
ReentrantLock中有3个内部类,FairSync和NonfairSync分别代表着公平锁和非公平锁的实现,他们父类是Sync
Sync继承自AQS
AQS中内部类Node
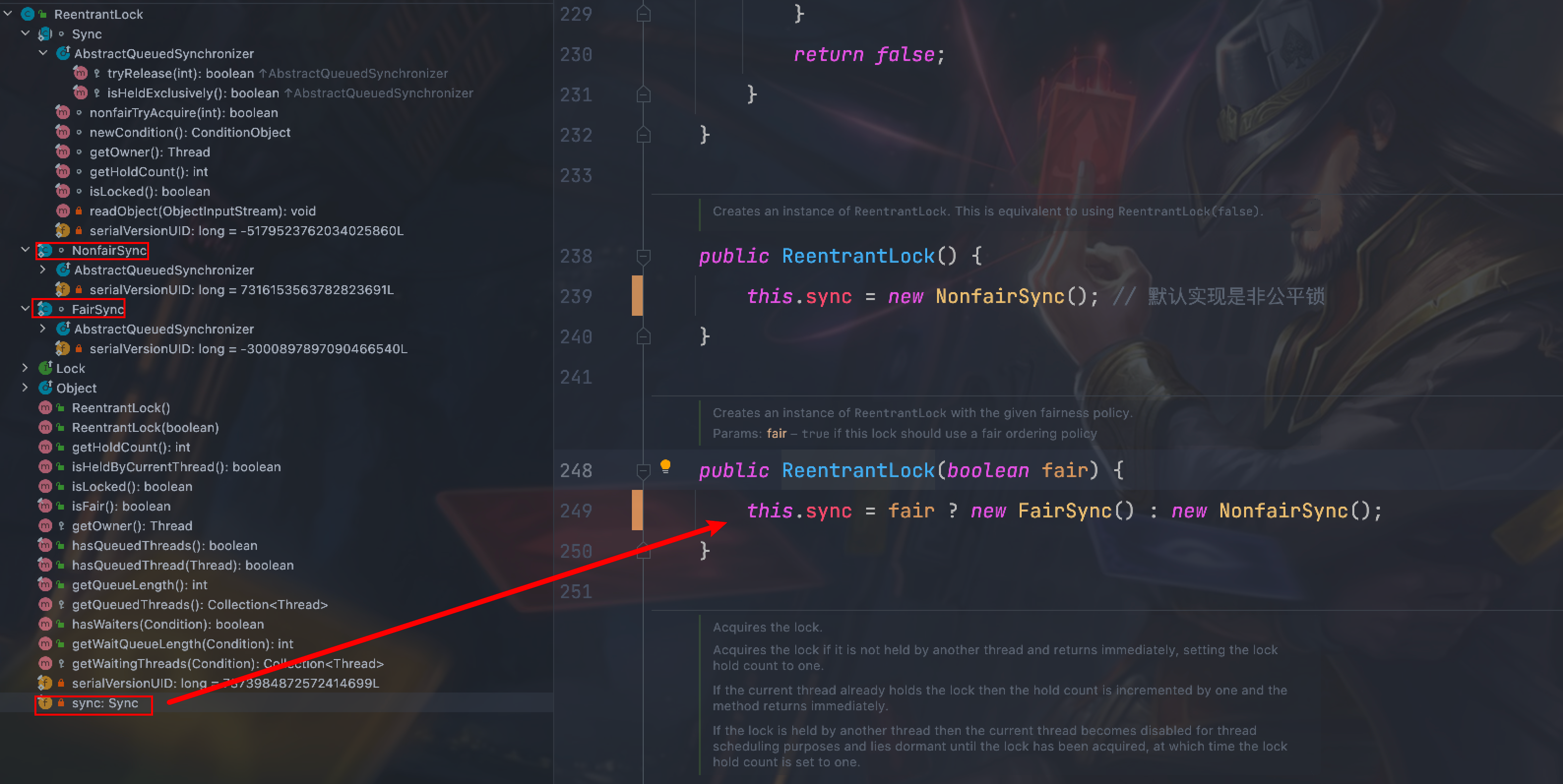
3.2 构造方法 ReentrantLock中属性sync,构造方法仅仅是指定sync是FairSync还是NonfairSync的实例,默认是NonFairSync
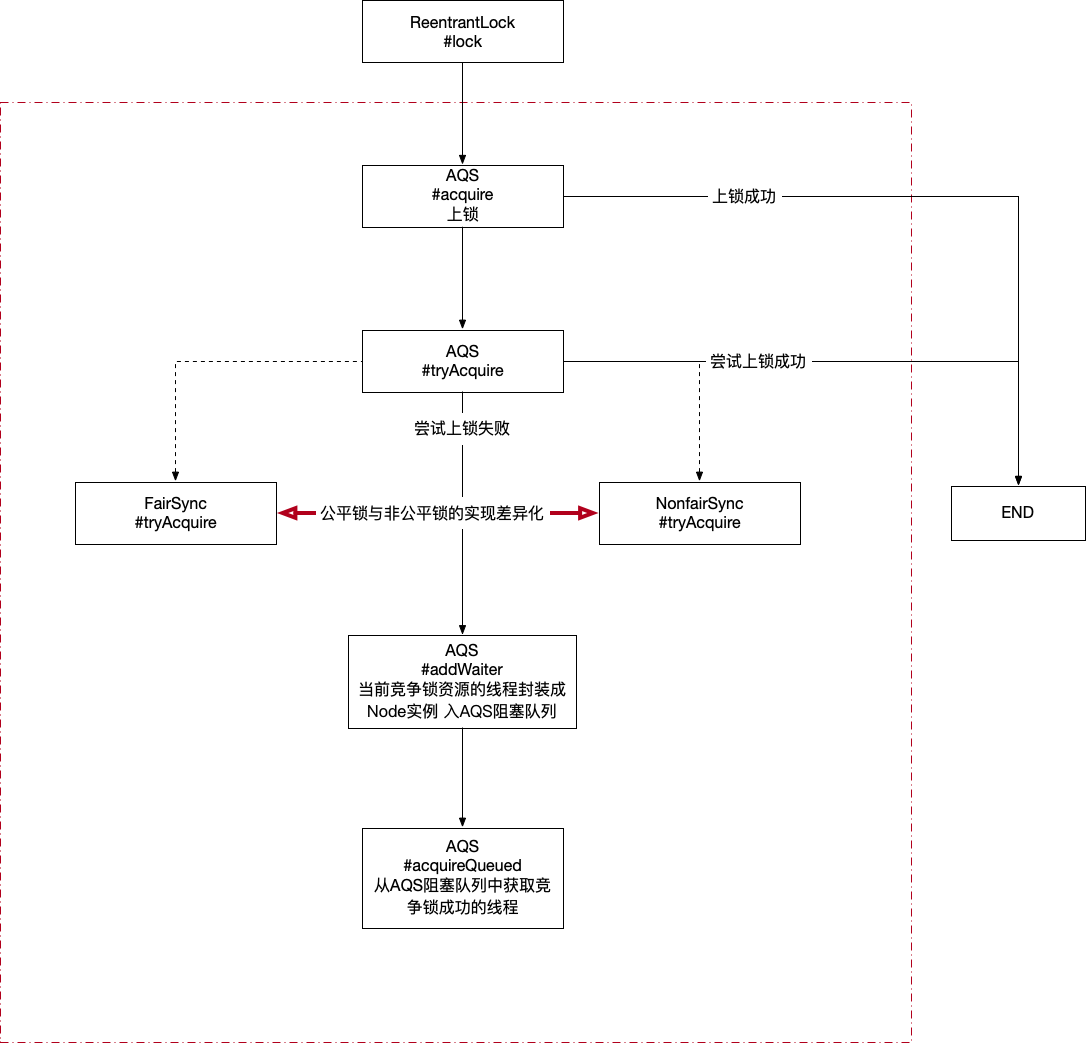
3.3 ReentrantLock#lock(…)方法 时序
3.3.1 AQS#acquire(…) 1 2 3 4 5 public final void acquire (int arg) {if (!this .tryAcquire(arg) &&this .acquireQueued(this .addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))this .selfInterrupt();
3.3.2 FairSync#tryAcquire(…) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 protected final boolean tryAcquire (int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();if (c == 0 ) { if (!super .hasQueuedPredecessors() && super .compareAndSetState(0 , acquires)) { super .setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true ;else if (current == super .getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0 )throw new Error ("Maximum lock count exceeded" );super .setState(nextc); return true ;return false ;
3.3.3 NonfairSync#tryAcquire(…) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 protected final boolean tryAcquire (int acquires) {return super .nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);final boolean nonfairTryAcquire (int acquires) {final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();if (c == 0 ) { if (super .compareAndSetState(0 , acquires)) { super .setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true ;else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0 ) throw new Error ("Maximum lock count exceeded" );super .setState(nextc);return true ;return false ;
3.3.4 AQS#addWaiter(…) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private Node addWaiter (Node mode) { Node node = new Node (mode); for (;;) { Node oldTail = this .tail;if (oldTail != null ) { if (this .compareAndSetTail(oldTail, node)) { return node;else { this .initializeSyncQueue();
3.3.5 AQS#acquireQueued(…) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 final boolean acquireQueued (final Node node, int arg) { boolean interrupted = false ;try {for (;;) {final Node p = node.predecessor();if (p == head && this .tryAcquire(arg)) { this .setHead(node); null ; return interrupted; if (this .shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node)) this .parkAndCheckInterrupt(); catch (Throwable t) {if (interrupted)this .selfInterrupt();throw t;